Algorithm/Baekjoon
[백준 10164 : JAVA] 격자상의 경로 / DFS + DP
팡트루야
2021. 4. 17. 17:29
문제
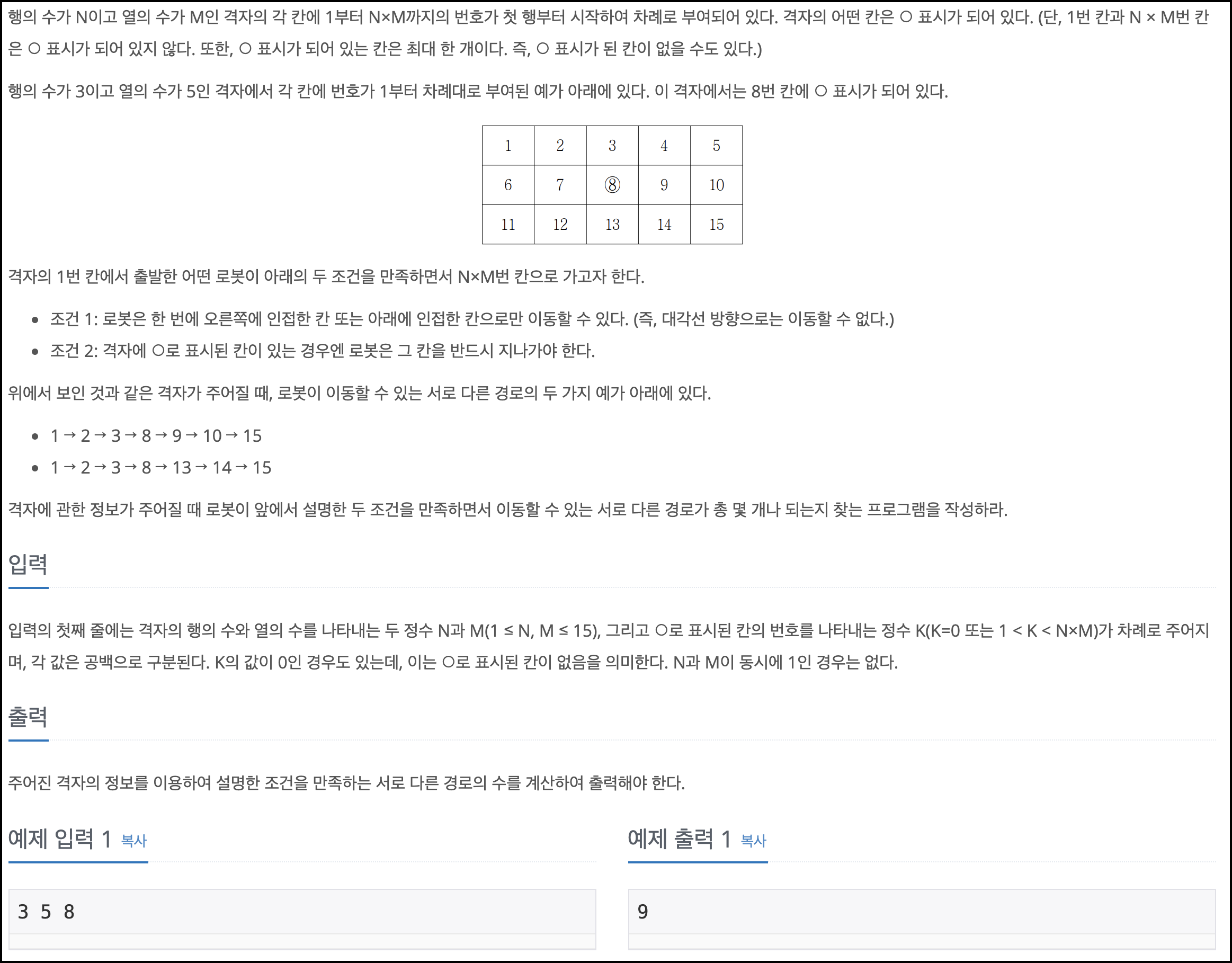
풀이
DFS + DP를 이용하는 기본유형의 문제다.
DFS 탐색으로 경로의 수를 찾을 때, 중복되는 탐색 내용이 무엇인지에 대한 이해만 있으면 충분히 풀 수 있는 문제.
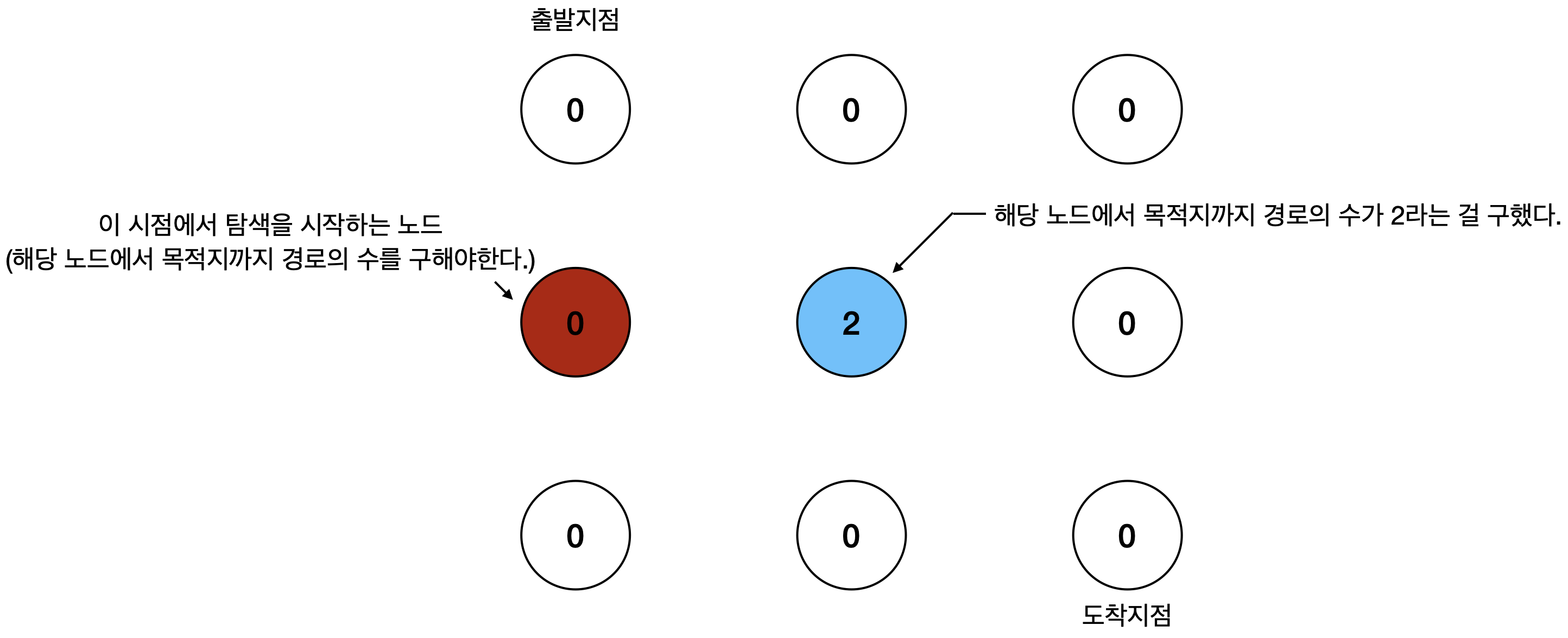
위 그림의 빨간색 노드(탐색을 진행 중인 노드)는 파란색 노드로 가는 탐색을 굳이 진행할 필요가 없다.
파란색 노드부터 목적지까지의 경로의 수를 이미 알기 때문이다.
위 개념만 제대로 이해하면, 나머지는 DFS로 탐색만 하면 쉽게 풀 수 있다.
코드
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
private static int N, M, K;
private static int[] dx = {0, 1};
private static int[] dy = {1, 0};
private static int[][] map, cache;
private static Node pass;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
K = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
cache = new int[N + 1][M + 1];
map = new int[N + 1][M + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= M; j++) {
map[i][j] = (i - 1) * M + j;
if (map[i][j] == K) {
pass = new Node(j, i);
}
}
}
int result;
if (K == 0) {
result = dfs(new Node(1, 1), new Node(M, N));
} else {
result = dfs(new Node(1, 1), pass) * dfs(pass, new Node(M, N));
}
System.out.println(result);
}
private static int dfs(Node cur, Node dst) {
if (cur.x == dst.x && cur.y == dst.y) {
return 1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
Node next = new Node(cur.x + dx[i], cur.y + dy[i]);
if (isValidRange(next, dst)) continue;
if (cache[next.y][next.x] != 0) {
cache[cur.y][cur.x] += cache[next.y][next.x];
} else {
cache[cur.y][cur.x] += dfs(next, dst);
}
}
return cache[cur.y][cur.x];
}
private static boolean isValidRange(Node pos, Node dst) {
return !(1 <= pos.x && pos.x <= dst.x && 1 <= pos.y && pos.y <= dst.y);
}
private static class Node {
int x, y;
public Node(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
}